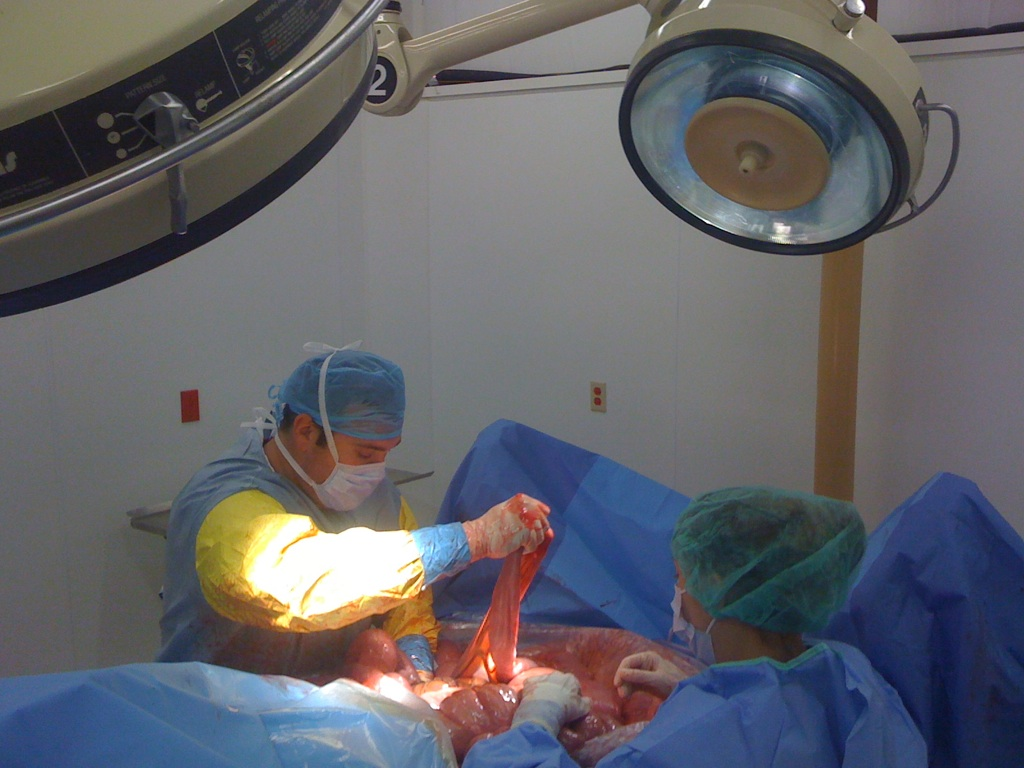
CALEC surgery, which stands for cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cells, represents a groundbreaking advance in eye surgery innovations aimed at treating corneal damage. Developed at Mass Eye and Ear, this procedure utilizes stem cell therapy to restore the corneal surface in patients suffering from blinding injuries. By extracting limbal epithelial cells from a healthy eye and transplanting them into the damaged eye, CALEC surgery has shown remarkable effectiveness, with success rates exceeding 90%. This innovative approach not only offers new hope for those with previously untreatable corneal conditions but also leads the way in blindness treatment by harnessing the potential of regenerative medicine. As research continues, CALEC surgery stands at the forefront of progressive treatments that could revolutionize ocular rehabilitation.
Cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cell therapy is an exciting development in modern ophthalmology, focusing on the regeneration of the corneal surface using the body’s own stem cells. This pioneering technique aims to address severe eye injuries that cause irreversible damage and vision loss, traditionally deemed challenging to treat. By utilizing healthy limbal stem cells, it provides a novel method of restoring function to the ocular surface, paving the way for improved outcomes for patients grappling with severe corneal damage. In this era of advancements in eye surgery, such therapies epitomize the convergence of science and patient care, creating new avenues for blindness treatment and corneal replenishment.
Understanding CALEC Surgery
Cultivated Autologous Limbal Epithelial Cell (CALEC) surgery represents a groundbreaking approach in the field of ophthalmology, specifically designed to address corneal damage. The process starts with harvesting limbal epithelial cells from a healthy eye, which are then cultivated in a laboratory to create a robust cellular graft. This innovative method not only revives the cornea’s surface but also promises a relatively high success rate in restoring vision for those with previously untreatable injuries. Research led by Mass Eye and Ear has shown that this technique has a remarkable over 90 percent effectiveness rate, which greatly enhances the hope for individuals suffering from severe ocular surface damage and even blindness due to corneal problems.
One of the key advantages of CALEC surgery is its personalized approach by using the patient’s own cells to regenerate the damaged corneal surface. This minimizes the risk of immune rejection that often occurs with donor tissues. Furthermore, in-depth clinical trials have demonstrated significant improvements in visual acuity among participants, marking a pivotal shift in how ocular injuries are treated post-trauma. The continuing advancements in eye surgery innovations like CALEC signify a transformative movement within regenerative medicine, potentially reshaping treatment standards for corneal damage.
Applications of Stem Cell Therapy in Eye Surgery
Stem cell therapy is revolutionizing eye surgery, particularly in treating complex conditions such as corneal injuries and degenerative eye diseases. The application of cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cells through CALEC surgery exemplifies the potential of stem cell therapies in restoring the eye’s health. Patients with limbal stem cell deficiency—often caused by injuries or diseases—have access to a novel solution that facilitates the regeneration of healthy corneal tissue, thereby alleviating pain and restoring sight. This innovation is especially pertinent given the limitations of traditional corneal transplants, which require compatible donor tissue that is not always readily available.
The success of stem cell treatments is indicative of a broader trend towards personalized medicine in ophthalmology. Treatments such as CALEC spotlight how tailored approaches can yield effective outcomes. As ongoing clinical research continues to develop, stem cell therapy is expected to expand its role in managing not just corneal damage, but a wide array of visual impairments. These advancements underscore the importance of investing in innovative medical research, as it holds the key to unlocking new solutions for chronic conditions that lead to blindness.
Innovative Techniques for Corneal Damage Treatment
Innovative techniques in corneal damage treatment are transforming the landscape of ophthalmology. The cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cell (CALEC) approach is at the forefront, providing new hope for patients with corneal injuries that were once deemed irreparable. By leveraging the regenerative properties of stem cells, this approach not only restores the cornea’s surface but also minimizes reliance on conventional methods that might not yield successful outcomes. As medical professionals like Ula Jurkunas engage in these pioneering studies, they pave the way for a future where complex eye conditions no longer lead to permanent blindness.
Additionally, advancements in surgical methods and therapies are complemented by ongoing research into cell manufacturing processes. The collaboration between Mass Eye and Ear and institutions like Dana-Farber ensures that these stem cell treatments meet rigorous quality standards before they reach patients. Continued efforts in refining these techniques will ultimately expand their applicability, potentially allowing for treatments that address bilateral corneal damage, thus widening the pool of patients who could benefit from these revolutionary therapies.
The Role of Limbal Epithelial Cells in Eye Health
Limbal epithelial cells play a critical role in maintaining corneal health and clarity. These specialized cells are responsible for repairing and regenerating the outer layer of the cornea, ensuring its smooth surface and protective function. When injuries or diseases deplete these cells, patients often experience complications such as scarring, chronic pain, and diminished visual acuity. Techniques like CALEC surgery are thus essential as they harness the regenerative capabilities of limbal epithelial cells to restore ocular surface integrity, providing a viable solution for those suffering from corneal damage.
Understanding the biology of limbal epithelial cells also informs future treatments for eye diseases. As researchers explore the mechanisms that underlie cell regeneration and repair, they open up new avenues for potential therapies aimed at preventing or reversing ocular damage. This knowledge is not only crucial for implementing effective interventions but also for developing comprehensive strategies to tackle conditions that can lead to blindness, reinforcing the importance of ongoing research in the field of ophthalmology.
Future Directions for CALEC Research
The future of CALEC surgery holds promising potential as researchers aim to broaden its applications and effectiveness. Current studies are already laying the groundwork for larger clinical trials that will involve a more diverse group of patients and multiple treatment centers. This expansion is vital for understanding the long-term outcomes of the procedure and refining techniques to enhance success rates. Researchers are planning to implement randomized controlled designs to demonstrate the efficacy of CALEC against existing treatment methods.
Moreover, future innovations may focus on developing allogeneic manufacturing processes using cadaveric donor limbal stem cells, which would allow for treatment options for patients with bilateral eye damage. This advancement could fundamentally change the scope of how corneal injuries are treated, enabling a broader population to benefit from regenerative therapies instead of navigating through painful and limited treatment choices. The intersection of stem cell research and clinical application continues to be an exciting frontier in the journey towards comprehensive solutions for visual impairment.
Impact of CALEC Trials on Patient Outcomes
CALEC trials have had a profound impact on patient outcomes, offering hope to those previously limited by corneal conditions. Early results from clinical studies indicate that approximately 93 percent of participants experienced improvements in their corneal surface, underscoring the procedure’s potential effectiveness as a treatment alternative. By focusing on the patient’s own stem cells, CALEC not only promotes healing but also significantly reduces the risks associated with transplanting foreign tissues. This approach fundamentally shifts the narrative for many patients who face the prospect of enduring visual impairment or even blindness.
The success observed in these trials is not just quantified by visual acuity; patients report enhancements in their quality of life, reflecting the holistic benefits of having their sight restored. As these trials progress and more data becomes available, they validate the relevance of stem cell therapies in contemporary medicine. The ongoing assessment of patient outcomes reinforces the importance of scientific inquiry in developing solutions that directly address the needs of individuals suffering from corneal pathologies.
Exploring the Safety Profile of CALEC Surgery
Safety is a paramount concern in any surgical intervention, and CALEC surgery has demonstrated a reassuring safety profile during its clinical trials. Notably, no serious adverse events have been reported among participants in the CALEC studies, indicating a high degree of tolerability of the procedure compared to traditional corneal treatments. This low incidence of complications is vital for patient acceptance and underscores the feasibility of implementing stem cell therapies into clinical practice.
Despite a few minor adverse events, such as transient infections, the overarching results from CALEC trials suggest that the benefits of restored vision and corneal health significantly outweigh the risks. As further studies are conducted, ongoing monitoring will be essential to ensure that the safety benchmarks are maintained, and any emerging concerns are addressed swiftly. Establishing trust in the safety of CALEC will likely facilitate more widespread adoption of this innovative technique in ocular surgery.
Regenerative Medicine and Its Potential in Ophthalmology
Regenerative medicine stands at the frontier of medical advancements, particularly in ophthalmology where it holds the potential to transform treatment paradigms. CALEC surgery exemplifies how regenerative strategies can address complex eye injuries through the innovative use of stem cells. This approach not only regenerates corneal tissues but also introduces a new dimension to treating conditions associated with blindness and vision impairment. The success of these stem cell therapies is inspiring a generation of researchers and clinicians to explore further regenerative options that could enhance patient outcomes.
The potential applications of regenerative medicine extend beyond corneal health; researchers are investigating various pathways to repair and regenerate other ocular structures. As scientific understandings deepen and methodologies improve, the integration of regenerative strategies into everyday clinical practice could reshape patient expectations and therapeutic outcomes. The ongoing exploration into the realm of stem cell therapy highlights the endless possibilities of regenerative medicine, providing a beacon of hope for preserving vision and improving the quality of life for patients worldwide.
Collaboration in Advancing Eye Surgery Innovation
The advancement of eye surgery innovations, particularly those involving CALEC and stem cell therapies, showcases the power of collaboration among leading medical institutions. The synergy between Mass Eye and Ear, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, and other research entities has been instrumental in bringing cutting-edge treatments from laboratory exploration to the clinical trial stage. This collaboration not only enhances the technical and scientific knowledge involved but also broadens the impact by allowing multiple experts to contribute to research and development efforts.
Such partnerships are essential not just for developing new surgical techniques but for establishing rigorous clinical frameworks that ensure safety and effectiveness. By pooling resources, expertise, and patient populations, collaborative efforts ensure that innovations undergo comprehensive evaluations. As the landscape of ophthalmological treatments continues to evolve, these interdisciplinary collaborations will be crucial in advancing the field and meeting the growing challenges associated with ocular diseases.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is CALEC surgery and its relevance to eye health?
CALEC surgery, which stands for cultivated autologous limbal epithelial cells, is an innovative eye surgery utilizing stem cell therapy to restore the cornea’s surface. This procedure is especially beneficial for patients with corneal damage due to injuries, infections, or chemical burns, where traditional treatments have failed.
How does the CALEC surgical procedure work?
The CALEC procedure involves extracting limbal epithelial cells from a healthy eye and expanding them into a graft. This graft is then transplanted into the damaged eye, allowing for the regeneration of the corneal surface, which helps restore vision and alleviate pain caused by corneal injuries.
What are the success rates of CALEC surgery based on recent studies?
Recent clinical trials indicate that CALEC surgery has a success rate of over 90% in restoring the cornea’s surface. Follow-up data showed that 50% of participants achieved complete restoration at three months, with success rates increasing to 79% and 77% at the 12 and 18-month evaluations, respectively.
Who can benefit from CALEC surgery?
CALEC surgery is primarily designed for patients suffering from limbal stem cell deficiency due to corneal damage. Patients must have only one affected eye to enable the harvesting of stem cells from the healthy eye, making it critical for those who have suffered trauma or serious ocular injury.
Is CALEC surgery currently available to all patients?
As of now, CALEC surgery remains experimental and is not widely available in the U.S. Further studies are needed before it can gain federal approval and be offered at hospitals like Mass Eye and Ear.
How does CALEC surgery compare to traditional corneal transplant methods?
Unlike traditional corneal transplants, which require a suitable donor cornea, CALEC surgery uses the patient’s stem cells to regenerate the corneal surface. This approach not only reduces the risk of transplant rejection but also offers a new hope for patients with previously untreatable corneal issues.
What are the future prospects for CALEC surgery?
The future of CALEC surgery looks promising, with ongoing research aimed at expanding its applicability — including developing allogeneic approaches to treat patients with damage to both eyes. Larger-scale studies are planned to support FDA approval and broaden access to this innovative treatment.
What are the potential risks associated with CALEC surgery?
While CALEC surgery has shown a high safety profile with minimal adverse events, like any surgical procedure, it may carry risks. Reported minor complications have included mild infections, but these typically resolved swiftly. Close monitoring during and after the procedure is essential to mitigate these risks.
How can CALEC surgery improve the quality of life for patients with corneal damage?
By restoring the corneal surface, CALEC surgery has the potential to significantly improve visual acuity and reduce pain in patients with corneal damage. The innovative use of stem cell therapy in this procedure offers new hope for a better quality of life for those previously considered untreatable.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Ula Jurkunas performs the first CALEC surgery at Mass Eye and Ear. |
| The clinical trial used stem cells from a healthy eye to restore corneal surfaces in 14 patients. |
| CALEC treatment showed over 90% effectiveness in restoring the cornea’s surface. |
| The procedure involves taking stem cells via biopsy, expanding them, and transplanting them into the damaged eye. |
| A significant portion (50% at 3 months, 79% at 12 months, and 77% at 18 months) achieved complete restoration of the cornea. |
| The treatment remains experimental and is not yet widely available. |
Summary
CALEC surgery represents a revolutionary advancement in treating previously untreatable corneal damage. This innovative procedure uses stem cells to repair the cornea and has demonstrated high success rates in restoring vision for patients suffering from severe ocular injuries. With ongoing research and the aim for wider application, CALEC surgery holds considerable promise for enhancing eye health and improving the quality of life for individuals affected by corneal injuries.