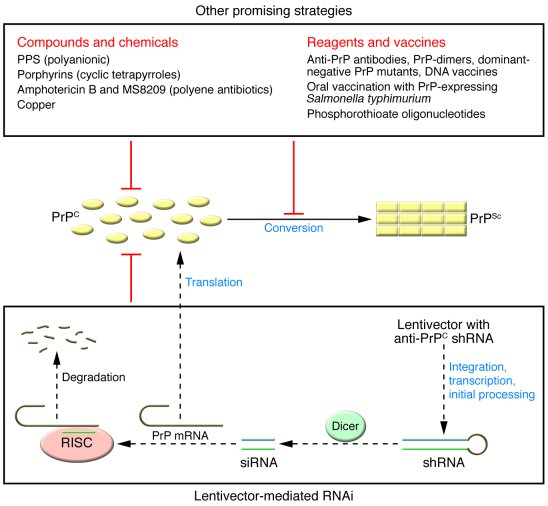
Prion disease treatment is on the brink of groundbreaking advancements, offering hope for those afflicted by these rare and devastating conditions. Recent research has highlighted the potential of gene editing therapy, which could revolutionize the management of prion diseases, including fatal familial insomnia and others characterized by misfolded proteins. These disorders have long been deemed untreatable, but a study published in *Nature Medicine* revealed promising results, showcasing recent breakthroughs in prion disease research. The innovative approach of altering genetic sequences presents a potential pathway to significantly reduce the accumulation of harmful proteins in the brain. Enthusiastic scientists, many with personal connections to these diseases, are driven to forge ahead on this critical journey toward effective therapies for patients facing a grim prognosis.
The exploration of therapies targeting prion-related conditions, commonly referred to as prion disorders, is gaining momentum as researchers push the boundaries of medical science. Among these conditions is fatal familial insomnia, a poignant reminder of the impact of genetic mutations on individuals and their families. As scientific inquiry progresses, many hope that solutions involving sophisticated techniques, such as gene editing, will emerge to combat these lethal afflictions. Ongoing studies reveal that innovative treatment strategies could lead to management options previously considered unattainable. With the scientific community rallying around the urgency of this mission, the landscape of prion disease treatment is evolving rapidly, promising newfound hope for those impacted.
Understanding Prion Diseases: An Overview
Prion disease refers to a group of rare and fatal neurodegenerative disorders primarily caused by the misfolding of prion proteins in the brain. This category includes various conditions such as Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker syndrome, and fatal familial insomnia. The underlying mechanism involves the transformation of normal prion proteins into a toxic, misfolded form that aggregates in the brain, leading to severe neuronal damage and cognitive decline. Understanding the genetic and molecular basis of these diseases is crucial for developing effective therapies.
Several studies indicate that both inherited and sporadic cases contribute to the prevalence of prion diseases. Approximately 15% of the cases are linked to genetic mutations, specifically in the prion protein gene, while the majority arise spontaneously. Ongoing research is focused on elucidating these mechanisms to pave the way for novel treatments. By targeting the genetic factors associated with prion diseases, researchers hope to mitigate the effects of these conditions, offering hope for those affected.
Recent Breakthroughs in Prion Disease Research
Significant advancements have recently emerged in the fight against prion diseases, particularly with the advent of innovative gene-editing technologies. A study published in Nature Medicine highlighted a groundbreaking approach utilizing base editing to target and alter the genetic underpinnings of prion diseases. This methodology has shown promise in reducing the concentration of harmful prion proteins in laboratory mice, resulting in increased lifespans. These findings represent a leap forward, demonstrating that genetic interventions might effectively counteract the devastating symptoms of prion disorders.
Furthermore, researchers at the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard are at the forefront of this revolutionary work, under the leadership of experts like David Liu. Their efforts exemplify collaborative science, as they incorporate knowledge from various disciplines to enhance the efficacy of gene-editing therapies. As these breakthroughs materialize, they instill hope in patients and families impacted by prion diseases, paving the way for clinical trials and potential treatments in the near future.
Ultimately, the exploration of gene-editing techniques not only highlights their role in prion disease treatment but also serves as a catalyst for more expansive studies on genetic conditions. As understanding grows, researchers can create tailored approaches that directly address the complexities of prion diseases.
The Role of Gene Editing Therapy in Treating Prion Diseases
Gene editing therapy stands at the forefront of innovative treatment strategies for prion diseases. By precisely targeting the genetic sequence responsible for producing harmful prion proteins, researchers aim to modify or correct the mutations that lead to these devastating conditions. The recent success in using base editing has shown that it is possible to effectively reduce toxic protein levels while increasing longevity in experimental models, offering encouraging results that might translate into viable human treatments.
Moreover, patient-scientists like Sonia Vallabh and Eric Minikel emphasize the personal stakes involved in this research. Their experiences with fatal familial insomnia inspire their determination to uncover new therapies that can save lives. This personal touch has fostered a deeper commitment to the scientific pursuit of gene editing as a method to halt the progression of prion diseases and improve patient outcomes. As research continues, the integration of patient feedback and perspectives will be crucial for ensuring the development of therapies that truly address the needs of those affected.
Collaboration and Motivation in Prion Disease Research
The collaboration among researchers in the field of prion disease treatment exemplifies the power of teamwork and shared motivation. With scientists from various backgrounds uniting to tackle the complexities of prion disorders, recent studies have yielded promising outcomes. The involvement of patient-scientists adds another level of urgency to this research, as they bring first-hand experience and emotional investment to the table. This dynamic fosters a unique environment where innovative ideas can flourish, ultimately driving progress toward effective therapies.
Additionally, the collaboration highlights the importance of multi-disciplinary approaches in medical research. Coupling expertise in genetics, neurology, and therapeutic development has proven fruitful in addressing the intricate mechanisms involved in prion diseases. As researchers continue to communicate and share insights, the potential for breakthroughs in treatment grows exponentially, underscoring the significance of collaboration in achieving shared goals in prion disease research.
Future Directions in Prion Disease Treatment
Looking ahead, the research community is optimistic about the potential for new therapeutic strategies in prion disease treatment. The recent discoveries involving gene editing are just the beginning; there is much more to explore regarding vectors, delivery methods, and safety protocols. As trials transition from preclinical models to potential human applications, researchers will need to ensure that these therapies can be administered effectively with minimal risk to patients. The focus will be on refining gene editing techniques and optimizing vector design to enhance precision in targeting prion proteins.
Moreover, future research efforts may involve expanding the focus beyond genetic therapies to include complementary approaches, such as immunotherapy and supportive care. A holistic treatment strategy will be essential to managing prion diseases effectively. Engaging with affected communities and maintaining communication with patient advocacy groups will ensure that the research aligns with the needs and preferences of those at risk, ultimately fostering patient-centric innovations in treatment.
The Personal Impact Behind Prion Disease Research
The personal stories of researchers involved in prion disease studies, particularly those who have familial ties to these conditions, significantly influence their work. For instance, Sonia Vallabh’s diagnosis of fatal familial insomnia has transformed her life into a mission not only for her own health but for all those suffering from prion diseases. This deeply personal connection fuels their dedication to scientific endeavors and drives them to seek impactful solutions that could potentially save lives. Their experiences serve to humanize the research process, reminding stakeholders of the real-world implications of scientific advancements.
This personal narrative can also enhance public awareness about prion diseases and the urgent need for research funding. Hearing firsthand accounts of those affected inspires empathy and urgency in the scientific community and beyond. As patient-scientists like Vallabh and Minikel share their journeys, they instill hope in countless individuals facing the trials of these fatal disorders, urging the scientific community to fast-track research efforts, ultimately striving for breakthroughs in prion disease treatment.
Enhancing Public Awareness of Prion Diseases
Raising public awareness about prion diseases and the challenges they pose is critical for fostering support for research and treatment initiatives. These disorders, though rare, have devastating effects on individuals and families, highlighting the importance of educating the public about symptoms, risk factors, and emerging research findings. Engaging in outreach through educational campaigns, community seminars, and social media can help demystify the complexities surrounding prion diseases and promote understanding of ongoing scientific efforts toward treatment.
Moreover, public support is essential for driving funding and resources toward prion disease research. Increased awareness can mobilize donations and grants, enabling researchers to pursue innovative studies like gene editing therapies. By encouraging open dialogue about prion diseases, researchers and advocates can create a more informed community, ultimately leading to accelerated progress in treatment development and patient care.
The Importance of Supporting Prion Disease Patients
The journey through a prion disease diagnosis can be incredibly challenging for both patients and their families. Supporting individuals affected by these disorders is paramount to improving their quality of life and providing necessary resources for coping with the disease. Offering comprehensive support services, including counseling, medical assistance, and educational resources, can greatly enhance the experience of patients navigating their diagnosis. This holistic approach helps ensure that patients feel cared for and understood.
Additionally, community support networks play a vital role in connecting patients and families who are facing similar realities. Resources such as support groups, informational websites, and patient advocacy organizations can provide comfort, solidarity, and essential knowledge. By fostering these supportive environments, the research community can address the emotional and psychological impact of prion diseases while simultaneously promoting awareness of ongoing treatments and breakthroughs.
Potential Challenges in Prion Disease Treatment Research
Despite the promising advancements in prion disease research, several challenges remain. The path to developing effective treatments is often fraught with complexities, particularly when dealing with the intricacies of prion proteins and their infectious nature. Researchers must navigate regulatory hurdles, safety concerns regarding clinical trials, and the inherent difficulties in working with rare diseases that might not attract robust funding compared to more prevalent disorders. Addressing these obstacles is critical to ensuring the continued progress of therapies aimed at treating prion diseases.
Moreover, translating success from laboratory models to human applications poses its own challenges. While laboratory results may yield encouraging data, replicating that success in human trials involves numerous variables, including dosage, patient variability, and long-term effects. Researchers must remain vigilant in addressing these issues, refining their approaches based on ongoing findings, and seeking collaboration with regulatory bodies to ensure that treatments advance safely and effectively into the clinical realm.
Frequently Asked Questions
What recent breakthroughs in prion disease treatment have been seen?
Recent breakthroughs in prion disease treatment include promising research published in Nature Medicine that demonstrated a gene-editing therapy capable of reducing harmful protein concentrations in laboratory mice by 50%. This advancement offers hope for effective treatments for fatal prion diseases such as fatal familial insomnia.
How does gene editing therapy work in the context of prion disease treatment?
Gene editing therapy in prion disease treatment involves altering the genetic code responsible for producing misfolded proteins that cause conditions like fatal familial insomnia. By precisely editing a single base in the relevant gene, researchers have been able to significantly reduce protein levels, thereby increasing the lifespan of affected mice by 52%.
What are prion diseases and how do they affect patients?
Prion diseases are a group of rare and fatal neurodegenerative disorders characterized by protein misfolding, leading to severe brain damage and dementia. Conditions such as Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and fatal familial insomnia fall under this category, and they can cause debilitating symptoms, ultimately resulting in death.
What is the relationship between fatal familial insomnia and prion disease treatment research?
Fatal familial insomnia is a genetic prion disease, and ongoing research into gene editing therapy aims to find effective treatments for patients like Sonia Vallabh, who has personally experienced its impacts. Her work and dedication have been pivotal in advancing the research towards potential treatments.
Are human clinical trials for prion disease treatment on the horizon?
While recent breakthroughs in gene editing therapies show promise for prion disease treatments, researchers caution that human clinical trials are still several years away. Extensive preliminary work must be conducted to refine the therapy and ensure safety before progressing to human testing.
What challenges remain in the research on prion disease treatment?
The research on prion disease treatment faces challenges such as ensuring the safety and efficacy of gene editing techniques, improving the delivery of the therapeutic vectors, and refining the base editing technology used in the experiments. These hurdles need to be addressed before any potential clinical applications.
How can the public stay informed about research on prion diseases and treatments?
The public can stay informed about research on prion diseases by following scientific journals like Nature Medicine, engaging with organizations dedicated to prion diseases, and following updates from research institutions such as the Broad Institute and leading researchers in the field.
What role do patient-scientists play in prion disease treatment research?
Patient-scientists, like Sonia Vallabh and Eric Minikel, play a crucial role in prion disease treatment research as they bring personal motivation and insight into the patient experience. Their involvement fosters collaboration and drives innovation in finding effective treatments for prion diseases.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Patient-Scientist Involvement | Sonia Vallabh, an HMS Assistant Professor of Neurology, is both a researcher and a patient with an inherited variant of prion disease, illustrating a personal stake in finding a treatment. |
| Gene-Editing Therapy | Recent studies show a gene-editing technique that can reduce harmful prion protein concentration in mice, leading to a significant increase in lifespan. |
| Research Collaboration | The collaboration between Vallabh, her husband Eric Minikel, and David Liu has been vital for the development of this promising approach to prion disease treatment. |
| Future Human Trials | Researchers emphasize that while the findings are promising, human clinical trials are still years away due to necessary steps in refining the therapy. |
Summary
Prion disease treatment has seen a significant breakthrough thanks to recent research exploring gene-editing therapies. This innovative approach shows potential in effectively reducing toxic prion proteins, evidenced by increased lifespans in laboratory mice. Researchers, including patient-scientist Sonia Vallabh, are motivated by personal experiences with the disease, highlighting the urgent need for effective treatments. Although human clinical trials are still a few years off, the developments offer hope for addressing these rare and fatal disorders.