Is sugar addictive? This question sparks significant debate among nutrition experts, given the increased sugar cravings that many individuals experience today. While substances like alcohol and nicotine are clinically classified as addictive, the health effects of sugar are often nuanced. The prevalence of sugar in processed foods not only contributes to compulsive eating but also leads to withdrawal-like symptoms when consumption is reduced. Understanding the potential for addiction-like behaviors is crucial for addressing the health implications tied to high sugar consumption.
When discussing the potential addictive nature of sugar, one might refer to it as a sweet stimulant or a craving catalyst. The effects of sugar on the brain can resemble those of other more recognized addictive substances, leading to habitual snacking and the continual desire for more. Moreover, many processed foods are engineered to enhance these cravings, making it difficult for individuals to regulate their intake. This relationship raises questions about our dietary habits and emphasizes the need to balance our enjoyment of sweetness with mindful consumption. Ultimately, exploring these alternatives brings us closer to understanding the real impact of sugary diets on our health.
Understanding Sugar Cravings and Their Impact on Health
Sugar cravings are a common phenomenon that many people experience. Often driven by the palatability of processed foods rich in sugar, these cravings can lead to compulsive eating behaviors. Understanding the health effects of sugar is crucial in managing these cravings. Notably, the average American consumes almost 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily, which is well above the recommended limits set by health organizations. The widespread availability of sugary snacks and beverages contributes to this overconsumption, raising concerns about long-term health implications such as obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases.
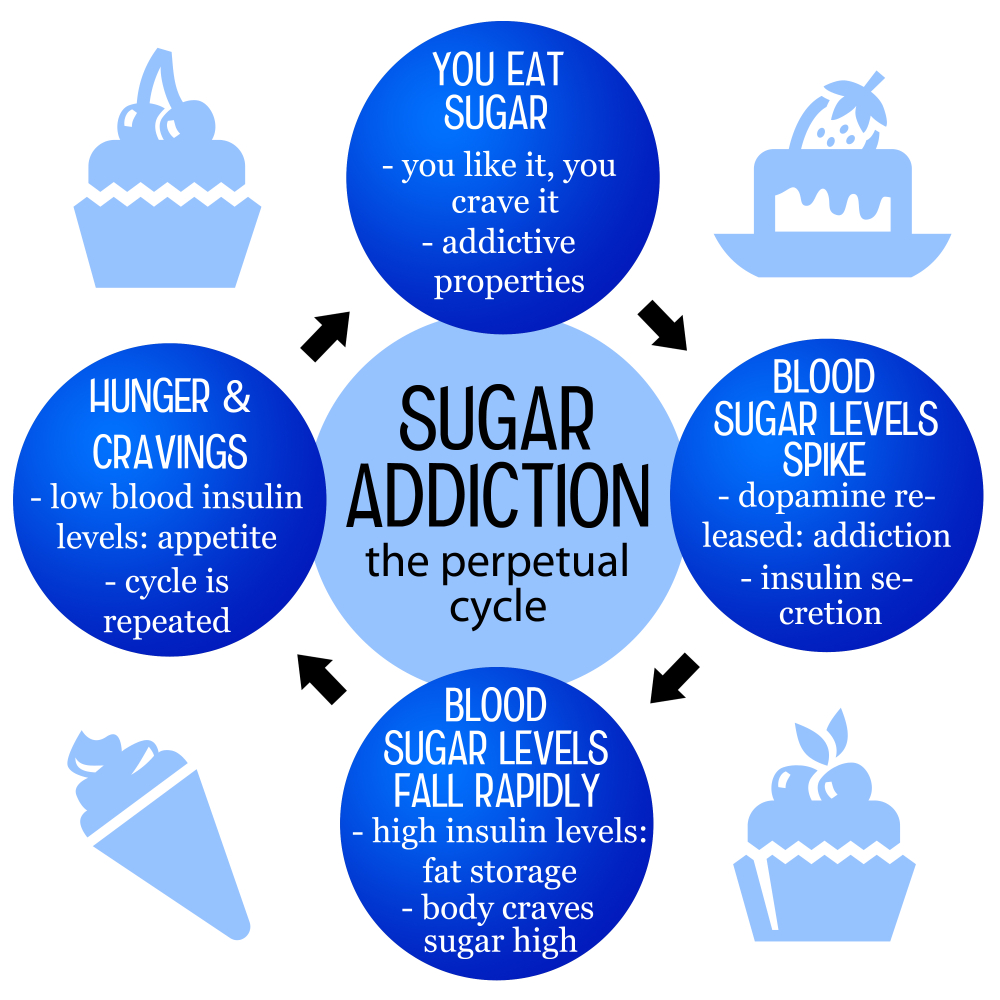
The craving for sugar often stems from a combination of biological and environmental factors. When you consume sugar, your brain rewards you with a dopamine surge, which can create a cycle of wanting more. This connection is similar to how addictive substances influence our reward system, raising debates about whether sugar should be classified alongside them. However, while sugar can enhance pleasure and texture in food, its effects on health necessitate mindful consumption. Moderating sugar intake can not only alleviate cravings but also contribute to better overall health.
Is Sugar Addictive? Examining the Evidence
The topic of whether sugar is addictive has sparked considerable debate among experts. While substances like alcohol and nicotine meet established criteria for addiction, sugar’s classification remains ambiguous. Research indicates that sugar can induce cravings and compulsive eating behaviors that mirror addiction, leading many to label it as addictive. However, sugar is a necessary component of our diet, found in a variety of nutritious foods such as fruits and vegetables, distinguishing it from traditional addictive substances that can be entirely eliminated from our lives.
Withdrawal-like symptoms, such as headaches and anxiety, can occur when individuals drastically reduce sugar intake, which may reinforce the perception of sugar as addictive. However, it is crucial to note that these symptoms are generally less severe than those associated with alcohol or drug withdrawal. For most individuals, moderate sugar consumption does not lead to significant health consequences. The key lies in understanding the appropriate amounts of sugar to consume and replacing high-sugar, processed foods with healthier alternatives.
The Role of Processed Foods in Sugar Cravings
Processed foods play a significant role in escalating sugar cravings. These foods are typically high in added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium, designed to be hyper-palatable. As a result, they can trigger intense cravings that make it difficult for individuals to resist consuming them. This is particularly concerning, as these products often lack the nutrients our bodies need, further perpetuating unhealthy eating patterns. Recognizing which foods contribute to these cravings is an essential step in managing sugar consumption effectively.
Moreover, the marketing and accessibility of processed foods create an environment that consistently encourages higher sugar consumption. Many people find themselves consuming sugary snacks out of convenience rather than necessity. To combat this, individuals should develop awareness about food labels and also focus on whole, unprocessed foods. By making strategic dietary choices and reducing reliance on processed options, individuals can not only minimize cravings but also improve their overall health and well-being.
Navigating Sugar in a Balanced Diet
While sugar can contribute to cravings, it’s essential to recognize the importance of maintaining a balanced diet. Sugars found in whole foods, such as fruits and dairy, offer nutritional benefits that processed sugary snacks do not provide. It’s critical to differentiate between naturally occurring sugars and added sugars. Incorporating natural sugars into meals can satisfy sweet cravings while also delivering essential nutrients and fibers that support overall health.
Finding the right balance in sugar consumption involves not just moderation, but also mindfulness. Reducing added sugars gradually rather than completely eliminating them can prevent withdrawal symptoms and lead to a more sustainable approach to dietary changes. This can enhance the pleasure derived from eating, making it easier to maintain a healthy diet that includes sweetness without overindulgence.
The Psychological Aspects of Sugar Cravings
Cravings for sugar are not solely based on physical triggers but also involve psychological aspects. Emotional factors such as stress, boredom, and mood can greatly influence sugar consumption. In times of stress, many individuals seek comfort in sweet treats, creating a cycle where food becomes a coping mechanism. Recognizing these triggers is essential for anyone looking to manage their sugar intake and develop healthier coping strategies.
Incorporating strategies such as mindful eating and finding alternatives to emotional eating can help break the cycle of sugar cravings. Engaging in activities that foster happiness and satisfaction without the need for sugary snacks can greatly assist in reducing dependence on these foods. Understanding these psychological aspects allows individuals to cultivate a healthier relationship with food, leading to reduced cravings and better health outcomes.
Health Effects of Excessive Sugar Consumption
Excessive sugar consumption is linked to various health risks, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart diseases. As the body processes high levels of sugar, it can lead to insulin resistance over time, significantly raising the risk of developing metabolic disorders. Additionally, sugary beverages are a significant contributor to the overall daily sugar intake, offering little in terms of nutritional value while adding countless calories.
Furthermore, studies have shown that high sugar diets can impact brain health, contributing to impaired memory and cognitive functions. It’s crucial to recognize that the health effects of sugar extend beyond physical appearance, as high sugar consumption can also affect mental well-being, leading to increased anxiety and depression. Therefore, it’s imperative to adopt a diet that is low in added sugars to mitigate these health risks.
Gradually Reducing Sugar Intake for Better Health
Gradually reducing sugar intake can be a highly effective strategy for managing cravings and improving health. For many individuals, the idea of eliminating sugar entirely can feel overwhelming and counterproductive, potentially leading to rebound cravings. Instead, taking small steps to decrease added sugars can result in a more sustainable lifestyle change and help individuals adjust their taste preferences over time.
For example, substituting sugary snacks with healthier options, like fruits or nuts, can satisfy cravings while providing essential nutrients. Utilizing natural sweeteners in moderation can also help ease the transition away from high-sugar foods. Ultimately, a gradual approach allows individuals to maintain pleasure in their eating experiences while fostering a healthier relationship with sugar.
Why We Need Some Sugar in Our Diets
Contrary to popular belief, sugar serves a functional role in our diets. It is a source of energy for our bodies, particularly in high-intensity exercise. Additionally, sugar can enhance the flavors of various foods, making meals more enjoyable. Acknowledging the benefits of sugar, while understanding the need for moderation, is essential for a balanced diet.
By incorporating naturally occurring sugars from whole foods, individuals can enjoy the sweetness they crave without adverse health effects. It’s important to view sugar through a balanced lens—appreciating its role in our diets while maintaining awareness of its potential risks through excessive intake. Finding this balance ensures that we can enjoy life’s sweetness without compromising our health.
The Future of Sugar Guidelines and Public Health
As awareness of sugar’s health implications increases, there is a growing call for more informative public health guidelines regarding sugar consumption. By highlighting the significant health risks associated with excessive sugar intake, health authorities can better educate the public on making informed dietary choices. These guidelines could promote healthier alternatives and emphasize the importance of moderation in sugar consumption.
Moreover, future discussions surrounding sugar should incorporate the perspectives of nutrition experts, policy-makers, and public health advocates. By working collaboratively, comprehensive strategies can be implemented to combat the obesity epidemic and foster healthier eating habits across various populations. This multi-faceted approach can aid in paving the way for a healthier future, where individuals are empowered to make wiser choices regarding their sugar intake.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive, and what are the health effects of sugar consumption?
Sugar is often described as having addictive qualities due to its ability to increase cravings and promote compulsive eating behaviors. While sugar is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine, its high presence in processed foods can lead to habitual consumption and withdrawal-like symptoms when eliminated suddenly. Understanding the health effects of sugar consumption, particularly high added sugar intake, is crucial for maintaining a balanced diet.
What are sugar cravings, and how do they relate to sugar addiction?
Sugar cravings can occur due to the palatability and accessibility of sugary, ultra-processed foods. These cravings resemble addiction-like behavior, although sugar is not classified as an addictive substance. Instead, the context of habitual sugar consumption and the body’s response to high sugar intake can create strong cravings that may feel addictive to some individuals.
Can processed foods and cravings lead to sugar addiction?
Processed foods are high in added sugars and can stimulate cravings, making it difficult for individuals to moderate their sugar intake. While these foods can reinforce habitual consumption patterns that mimic addiction, sugar itself is not scientifically labeled as an addictive substance. Thus, managing the amount of processed sugars one consumes is key to reducing cravings.
What should I know about the health effects of sugar and addictive behaviors?
Excessive sugar consumption has been linked to various health issues, including obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. While it increases cravings akin to addictive behaviors, it is essential to differentiate between necessary dietary sugars found in whole foods and added sugars in processed foods, which can elicit more pronounced cravings and compulsion.
How does sugar consumption trigger cravings similar to addictive substances?
Sugar consumption can lead to a release of dopamine in the brain, similar to addictive substances. This reaction reinforces the desire to consume sweets, resulting in cravings. However, unlike addictive drugs, sugar is not wholly detrimental; moderate amounts can enhance dietary enjoyment without significant health consequences.
What are the recommendations for sugar intake to avoid addictive tendencies?
To avoid potential addictive tendencies related to sugar, the American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar intake to no more than 9 teaspoons for men, 6 teaspoons for women, and less for children. Monitoring sugar consumption and being mindful of the amount in processed foods can help manage cravings effectively.
Is it possible to experience withdrawal symptoms from stopping sugar consumption?
Yes, some individuals may experience withdrawal-like symptoms, such as headaches, anxiety, and dizziness when they stop consuming sugar abruptly. This highlights the compulsive eating behaviors sugar can induce, though it’s important to recognize these symptoms are less severe compared to those associated with true addictive substances.
| Key Point | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Sugar’s Addictive Nature | While sugar can increase cravings and compulsive eating behaviors, it is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. |
| Effects of Ultra-Processed Foods | Foods high in added sugar, unhealthy fats, and sodium can enhance cravings, leading to habitual consumption. |
| Withdrawal Symptoms | Stopping sugar abruptly can cause withdrawal-like symptoms, such as headaches and anxiety. |
| Need for Sugar | Sugar is a necessary part of our diet found in various healthy foods, unlike other drugs that can be eliminated entirely. |
| Recommended Sugar Intake | The American Heart Association recommends no more than 9 teaspoons for men and 6 for women of added sugar. |
| Gradual Reduction | Reducing sugar intake gradually is advised to prevent adverse effects. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? The debate surrounding sugar’s addictive qualities is complex and ongoing. Although it is not classified as an addictive substance by clinical standards, sugar can lead to cravings and compulsive behaviors similar to those observed with food addiction. While we need sugar for essential bodily functions, the excessive intake from processed foods poses health risks. Understanding the effects of sugar and managing our consumption with moderation will help prevent potential health issues while still enjoying the sweetness in our lives.