Pregnancy-related deaths represent a significant public health concern, with the United States experiencing a disturbing increase in the maternal mortality rate in recent years. Studies show that over 80 percent of these pregnancy-related deaths are preventable, highlighting the urgent need for enhanced prenatal and postpartum care. Disparities in access to healthcare services further compound the crisis, affecting marginalized communities disproportionately and illustrating stark health disparities across racial and ethnic lines. The alarming rise in maternal fatalities from conditions like cardiovascular diseases underscores the necessity for comprehensive care strategies that extend beyond the immediate postpartum period. As the nation grapples with increasing rates of preventable pregnancy deaths, it is imperative that we reevaluate our health systems to ensure that safe and equitable maternal healthcare is accessible to all.
Maternal health crises are often framed in terms of pregnancy-related fatalities, yet these issues encompass a broader spectrum of maternal outcomes. When discussing mortality in childbirth, one cannot ignore the underlying factors contributing to preventable pregnancy deaths, which are exacerbated by weak prenatal care and limited postpartum support. The sharp rise in maternal mortality statistics illustrates not only the fragility of healthcare access but also the urgent need to address systemic healthcare disparities faced by various communities. Solutions extending from improved access to quality prenatal services to comprehensive postpartum care could significantly reduce the preventable pregnancy deaths currently witnessed. It is vital to create a healthcare system where every woman has the opportunity to receive equitable care throughout her reproductive journey.
The Rising Toll of Pregnancy-Related Deaths in the U.S.
In recent years, the United States has grappled with a disturbing trend: the increasing rate of pregnancy-related deaths. A staggering over 80% of these fatalities are reported as preventable, reflecting deep-rooted issues within the healthcare system. Statistically, from 2018 to 2022, the maternal mortality rate surged alarmingly, with 2021 witnessing the sharpest increase, likely exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic. The statistics paint a worrisome picture, highlighting that maternal mortality affected vulnerable populations disproportionately, with American Indian and Alaska Native women suffering the most dire consequences.
Understanding why the U.S. leads among high-income countries in maternal mortality reveals an intricate web of factors. The nation features a fragmented healthcare system alongside significant health disparities influenced by race and socioeconomic factors. Innovative approaches and targeted policies are essential to bridge the widening gap in health outcomes, especially as the data indicates that pregnancy-related deaths differ dramatically by state due to varying access and quality of care. More concerted efforts to address these inequities could dramatically save lives.
Exploring Maternal Mortality Rates: Causes and Disparities
Maternal mortality rates in the U.S. pose serious public health challenges, showcasing alarming disparities across different racial and ethnic groups. The study under discussion reveals that systemic issues such as bias, inequitable healthcare access, and the presence of maternity care deserts contribute significantly to these disparities. For instance, while white women reported a maternal mortality rate of 27.6 per 100,000 live births, the rate for American Indian and Alaska Native women soared to an astonishing 106.3, highlighting a stark and unacceptable inequality.
The existence of such disparities necessitates a multifaceted approach to healthcare reform, focusing on enhancing prenatal and postpartum care. Addressing underlying health conditions like hypertension, which have become increasingly prevalent among younger women, is vital to improving maternal health outcomes. Policymakers need to prioritize investments in quality care tailored to the unique challenges faced by historically marginalized populations, ensuring that no woman is left behind regardless of her racial or socioeconomic background.
The Importance of Prenatal Care in Reducing Risks
Prenatal care plays a crucial role in ensuring the health of both mother and child, acting as the first line of defense against potential complications during pregnancy. Comprehensive prenatal check-ups enable healthcare providers to monitor health conditions proactively, which can prevent the distressing outcome of pregnancy-related deaths. Research indicates that consistent access to quality prenatal services is paramount in averting complications such as gestational diabetes or hypertension, which may lead to fatal outcomes when ignored.
The focus, however, must not only remain on early interventions but also extend into the postpartum period. Many women underestimate the significance of continued healthcare after childbirth, a misconception that can have dire implications. The growing acknowledgment of postpartum care as a critical component of maternal health emphasizes the need for ongoing support and monitoring, ensuring that mothers receive the necessary interventions well beyond the traditional six-week postpartum check-up.
Health Disparities: A Growing Concern
Health disparities have remained persistent issues in the U.S. maternal health landscape, revealing stark differences in outcomes based on race, ethnicity, and economic status. These disparities lead to an inequitable distribution of critical health resources, contributing to alarming maternal mortality rates among minority populations. It’s crucial to highlight these inequalities to develop targeted public health initiatives that confront systemic barriers and facilitate equitable healthcare access for all women.
Addressing these disparities requires comprehensive policy changes that encompass a multitude of factors influencing maternal health. From improving educational initiatives around reproductive health to increasing funding for community health programs, there are various avenues to pursue. Strategies must center around collaboration between healthcare providers, policymakers, and community organizations to ensure that all women receive the quality prenatal and postpartum care necessary to safeguard their maternal health.
The Role of Extended Postpartum Care
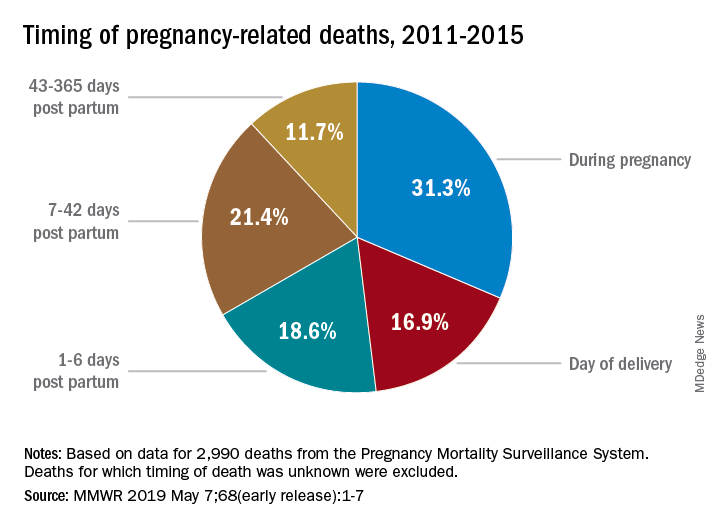
Extended postpartum care is emerging as a fundamental aspect of maternal health that has been historically overlooked in the U.S. healthcare system. The notion that the postpartum period ends at six weeks is a misconception that can lead to maternal complications if underlying health issues are left unmanaged. Recent research highlights that nearly one-third of maternal deaths occur between 42 days and one year postpartum, demonstrating the urgent need for improved postpartum care strategies.
Developing support systems that incorporate extended postpartum care involves fostering healthcare policies that prioritize the needs of mothers during this vulnerable period. Implementing comprehensive follow-up care that addresses mental health, physical recovery, and chronic disease management is essential to reduce postpartum-related deaths. By treating postpartum care as a continuum rather than a finite period, healthcare providers can create more supportive environments that promote long-term maternal health.
Chronic Conditions and Maternal Health
The rising incidence of chronic conditions such as hypertension among pregnant women has serious implications for maternal health outcomes. Cardiovascular disease has shifted to become the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths, as evidenced by the latest findings. Increased rates of chronic health conditions in younger populations present a concerning trend that requires immediate attention and targeted interventions to improve overall maternal healthcare.
Addressing chronic conditions during pregnancy entails establishing comprehensive screening and management protocols. Healthcare systems need to be equipped to identify high-risk individuals early and provide tailored interventions throughout the pregnancy journey. A focus on patient education and lifestyle modifications can empower women to better manage their health, ultimately leading to improved maternal health outcomes and the prevention of potential fatalities.
The Impact of Policy on Maternal Health Outcomes
Public health policies play a pivotal role in shaping maternal health outcomes across the nation. The significant disparities in maternal mortality rates by state underscore the urgent need for policy changes aimed at enhancing access to quality care. For instance, states like California have demonstrated that effective policies can lead to better health outcomes, suggesting that other states can replicate successful models to reduce their mortality rates.
Advocacy for policy reform must center around increasing funding for maternal health initiatives and ensuring equitable access to care services, especially for marginalized communities. The data indicates that without substantial investment and commitment to reforming these policies, the nation will continue to see a rise in preventable pregnancy deaths. Elevating maternal health as a public health priority is essential to shifting the narrative towards improved outcomes.
Awareness and Education: Key to Prevention
Increasing awareness and education regarding maternal health is essential for preventing pregnancy-related deaths. Providing expectant mothers with comprehensive information about prenatal and postpartum care can empower them to seek timely medical attention and advocate for their health. Educational programs targeting at-risk populations can help bridge the knowledge gap that often contributes to poor health outcomes, ensuring all women understand the importance of regular health check-ups.
Moreover, community outreach initiatives can play a crucial role in fostering awareness about chronic health conditions that may adversely impact pregnancy. This proactive approach can help women recognize warning signs and understand the significance of managing underlying health issues, ultimately improving their care-seeking behavior and reducing the overall maternal mortality rate.
Investing in Public Health Infrastructure for Maternal Care
The foundation of effective maternal health outcomes lies in a robust public health infrastructure designed to monitor and support individuals throughout their pregnancy journey. Strengthening this infrastructure is essential for enhancing data collection and sharing best practices among states. Policymakers must prioritize investments in maternal health resources to ensure that women receive the comprehensive care they need before, during, and after childbirth.
Inadequate funding and a lack of prioritization for maternal health initiatives can jeopardize progress towards reducing pregnancy-related deaths. Therefore, mobilizing resources and community support is critical for establishing a well-rounded approach to maternal healthcare. Establishing a national framework to address maternal health disparities can ensure consistent best practices are implemented and sustained, ultimately saving lives.
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors contribute to the high maternal mortality rate and pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S.?
The U.S. has a high maternal mortality rate and pregnancy-related deaths due to several factors, including a fragmented healthcare system, systemic bias, and inequitable healthcare policies. Additionally, the rise in chronic medical conditions such as cardiovascular disease among reproductive-age individuals contributes significantly to these deaths.
How can improving prenatal care impact pregnancy-related deaths?
Enhancing prenatal care is crucial in reducing pregnancy-related deaths. Proper prenatal care can identify risk factors early, manage chronic conditions, and ensure mothers receive necessary medical interventions, ultimately lowering the maternal mortality rate.
What steps can be taken to address health disparities related to pregnancy-related deaths?
Addressing health disparities involves targeted policy reforms that ensure equitable access to quality maternal care across different demographic groups. Investing in community health resources, improving healthcare access for underrepresented populations, and training healthcare providers to recognize and combat biases are essential steps.
What role does postpartum care play in preventing pregnancy-related deaths?
Postpartum care is vital for monitoring women’s health after childbirth, particularly in the first year post-pregnancy. With nearly a third of pregnancy-related deaths occurring during this period, improving postpartum care can prevent late maternal deaths and ensure ongoing support for new mothers.
Why is raising awareness about preventable pregnancy deaths important?
Raising awareness about preventable pregnancy deaths is critical in advocating for better healthcare policies and practices. With over 80% of these deaths deemed preventable, highlighting the issue can mobilize efforts to enhance prenatal and postpartum care, thus saving lives and improving maternal health outcomes.
How does the maternal mortality rate vary by state and demographics in the U.S.?
The maternal mortality rate varies significantly across states and demographics, with notable disparities observed among racial and ethnic groups. For instance, American Indian and Alaska Native women experience the highest pregnancy-related deaths, underscoring the need for state-specific interventions to improve health outcomes.
What are the leading causes of pregnancy-related deaths in the United States?
Cardiovascular disease has been identified as the leading cause of pregnancy-related deaths, accounting for over 20% of cases. Other significant contributors include hemorrhage, hypertensive disorders, and mental health conditions, highlighting the complexity of factors affecting maternal mortality.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| High U.S. Maternal Mortality Rate | The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries, with rates rising from 25.3 deaths per 100,000 live births in 2018 to 32.6 in 2022. |
| Preventability of Deaths | Over 80% of pregnancy-related deaths are preventable, indicating a need for better healthcare solutions. |
| Racial Disparities | American Indian and Alaska Native women face the highest maternal mortality rates—106.3 per 100,000 live births—compared to white women at 27.6. |
| Impact of COVID-19 | The sharpest increase in maternal mortality rates was recorded in 2021, correlating with the COVID-19 pandemic. |
| Leading Causes of Death | Cardiovascular disease accounts for over 20% of pregnancy-related deaths, a shift from previous leading causes like hemorrhage. |
| Late Maternal Deaths | Late maternal deaths, occurring between 42 days and 1 year postpartum, account for nearly one-third of total maternal deaths. |
| Need for Healthcare Improvement | Investment in public health infrastructure and innovative solutions is necessary to reduce pregnancy-related deaths. |
Summary
Pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. highlight a public health crisis, as the country consistently ranks highest among high-income nations in maternal mortality rates. Despite over 80% of these deaths being preventable, systemic issues within the healthcare system contribute to rising mortality rates, especially among racial minorities. Addressing these disparities through improved prenatal and postpartum care, along with comprehensive healthcare reforms, is crucial in reversing this troubling trend.